ok, so bouncing
when it bounces up, it bounces up
so we double the summation
but for the initial bounce, it only goes down
so we double the whole thing and minus the first bounce
the summation of the geometric sequence where the initial term is
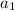
and the common ratio is r and the term is n is
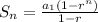
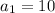
,
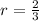
and n=30
double and minus 10
![2S_(30)-10=2(\frac{10(1-((2)/(3))^(30))}{1-(2)/(3))-10]()
the total distance traveled is
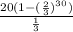
it simplifies to
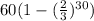
that's the answer is exponential notation