For this case we have that an identity is an equation in which the left side of the equation is equal to the right side of the equation.
We then have the following equation:
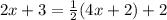
When applying the distributive property on the right side we have:
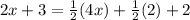
Rewriting we have:
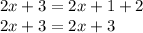
We observe that both sides are equal. Therefore, the equation is an identity.
Answer:
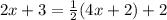
Option C