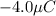Use the Coulomb's Law to find the other charge:
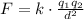
Where k is the Coulomb's constant:
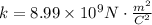
Isolate one of the charges from the equation:
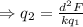
Substitute d=0.1m, F=14.4N, q_1=-4.0μC and the value of k:
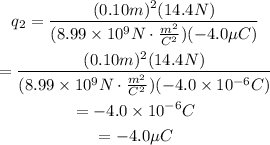
Notice that since the force is repulsive, both chargest must have the same sign.
Therefore, the answer is: