Answer:
A positive discriminant shows that the quadratic equation
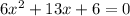 has two distinct real number solutions namely
has two distinct real number solutions namely
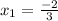 or
or
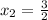
Explanation:
Consider the given Quadratic equation
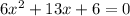
Discriminant is a part of quadratic formula that shows the nature of root for a given quadratic equation.
Quadratic formula for a general quadratic equation of the form
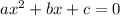 is given as:
is given as:
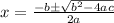 ......(A)
......(A)
Where,
 is the discriminant. .......(1)
is the discriminant. .......(1)
The discriminant can be positive, zero, or negative.
A positive discriminant shows that the quadratic equation has two distinct real number solutions.
A discriminant of zero shows that the quadratic equation has a repeated real number solution.
A negative discriminant shows that neither of the solutions are real numbers.
Given Quadratic equation
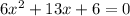
Here, a= 6 , b=13, c= 6
Put in (1) ,

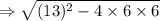
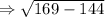
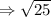
Thus, a positive discriminant shows that the quadratic equation has two distinct real number solutions.
Roots can be find as, Using (A)
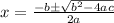
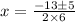
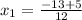 or
or
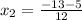
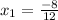 or
or
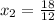
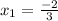 or
or
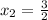
Hence, the system has two distinct real roots.