The average velocity of a gas, which behaves as an ideal gas, is calculated by the following equation:
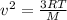
Where,
v^2 is average velocity squared
R is a constant = 0.08206atm.L/mol.K
T is the temperature of the gas, in Kelvin
M is the molar mass of the gas
We see that the velocity depends on the mass and the temperature. Since all the gases, in this case, have the same temperature the velocity will depend only on the molar mass.
The relationship between velocity and molar mass according to the formula is inversely proportional. That is to say that if the molar mass increases the velocity decreases and if the molar mass decreases the velocity increases.
Therefore, among the options, the gas with the highest average velocity will be the one with the lowest molar mass. Let's see what the molar mass of each gas is:
Cl2:70.91g/mol
CH4:16.04g/mol
NH3:17.03g/mol
The gas with the lowest molar mass is CH4, therefore this will be the gas with the highest average velocity.
Answer: CH4