Answer:
the astronaut will experience his weight 1/6 times smaller than the weigh near the surface of earth
Step-by-step explanation:
As per Newton's II law we know that net force on an object is given by the product of mass and acceleration
so here we have
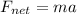
now we know that acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is 1/6 times the acceleration near the surface of earth
so we will have
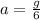
now the force near the surface of moon on an astronaut is given as
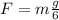
so the astronaut will experience his weight 1/6 times smaller than the weigh near the surface of earth