Hello!
Data:
Vo (initial volume) = 8 L
V (final volume) = ?
Po (initial pressure) = 101 kPa
P (final pressure) = 213 kPa
We have an isothermal transformation, that is, its temperature remains constant, if the volume of the gas in the container decreases, so its pressure increases. Applying the data to the formula, we have:
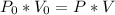
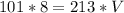
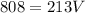
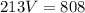
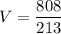
 I Hope this helps, greetings ... DexteR!
I Hope this helps, greetings ... DexteR!