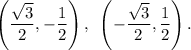Answer: The representation of the point in Cartesian co-ordinate system is
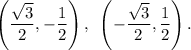
Step-by-step explanation: We are given to find the other representation of the point
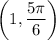 in Cartesian system
in Cartesian system
We know that
if (x, y) are the co-ordinates of a point in two dimensional XY-plane and (r, Θ) are the co-ordinates of the point in polar co-ordinate system, then we have the following relations:
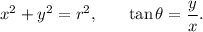
Given that
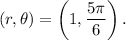
Therefore, we have
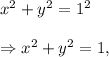
and
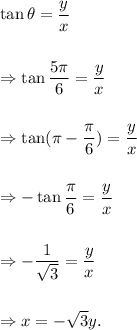
So,
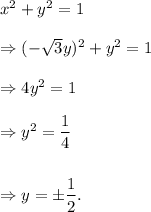
And,
When
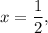 ,
,
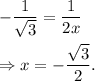
When
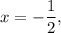 ,
,
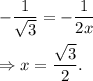
Thus, the representation of the point in Cartesian co-ordinate system is