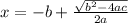Answer:
See below.
Explanation:
We are going to take the quadratic formula ax²+bx+c=0
a.Divide all terms in the equation by a.
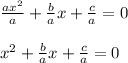
b.Subtract the constant (the term without an x) from both sides.
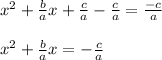
c.Add a constant (in terms of a and b) that will complete the square.
![x^(2) +(b)/(a)x=-(c)/(a)\\\\[tex]x^(2) +(b)/(a)x+(b^(2) )/(4a^(2) ) =-(c)/(a) +(b^(2) )/(4a^(2))\\\\(x+(b)/(2a)) ^(2) =(-4ac+b^(2) )/(4a^(2) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/college/im0ztegakiehyl5h44smaqat8qyhs7qlp9.png)
d.Take the square root of both sides of the equation.
![x+(b)/(2a) =[tex]\\x+(b)/(2a) =\frac{\sqrt{-4ac+b^(2) } }{2a}\\x=\frac{\sqrt{-4ac+b^(2) } }{2a}-(b)/(2a)](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/college/z7d51a3vtmn9w1kqb2r1dn90pfb80y884n.png)
e.Solve for x.