Explanation:
The equation of a moving object in physics is given by :
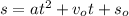 ...........(1)
...........(1)
Where
s₀ is the starting position of an object
a is the acceleration of the object
v₀ is the initial velocity of the object
t is the time taken
We need to find the value of acceleration by rearranging equation (1). Subtract
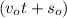 on both sides of equation (1) as :
on both sides of equation (1) as :
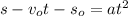
Divide both sides of above equation by t² as :
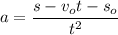
So, the value of acceleration is
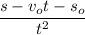 . Hence, this is the required solution.
. Hence, this is the required solution.