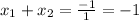Answer:
The sum of the roots of the equation
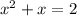 is -1
is -1
Explanation:
You have two options to find the sum of the roots,
- The first option is to use the Quadratic Formula to find the two roots:
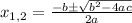
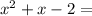 where:
where:
a = 1
b = 1
c = -2
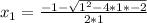 = -2
= -2
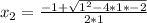 = 1
= 1
The sum of the roots is -2 + 1 = -1
2. The second option is use the fact that a general quadratic equation is in the form of:
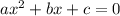
if you divided by
 you get:
you get:
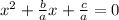
and always the sum of roots will be given for this expression
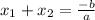
Why this is true?
Because if we use the Quadratic Formula as follows:
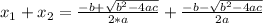
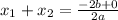
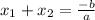
In the case of this equation: