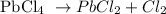The group IV elements are:
Carbon (C)
Silicon (Si)
Germanium (Ge)
Tin (Sn)
Lead (Pb)
The reason why they exhibit two oxidation states is because they have the following outer electronic structure (n being the period number):
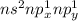
Closer to the bottom of the group it is harder for the 2 electros in the s orbital to be involved in bonding. This is known a the inert pair effect and it is explained because when the atoms in group 4 lose the p electrons they contract, drawing the electrons closer to the nucleus, makeing it more energetically difficult to remove the s electrones.
This effect is greater with heavier elements.
Therefore the most common oxidation state for carbon (the lighter element of the group) is +4.
An example is the formation of carbon tetrachloride:
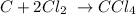
For lead (a heavier element) the most common oxidation state is +2. An example is the decomposition of Lead(IV) chloride: