Answer:
C. Gravity = air resistance
Step-by-step explanation:
An object falling down has two forces acting on him:
- Gravity, which acts downward --> the magnitude of this force is constant (equal to
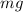 , where m is the mass of the object and g is the gravitational acceleration)
, where m is the mass of the object and g is the gravitational acceleration)
- Air resistance, which acts upward --> the magnitude of this force is directly proportional to v, the speed of the object
When the object starts its fall, the speed is zero (v=0) so only gravity acts and it accelerates the object downward. Therefore, the speed of the object increases, and so does the air resistance, until a point where the air resistance becomes equal to gravity (which is constant): when this occurs, the acceleration of the object becomes zero (because forces are balanced), so the object continues its fall at constant velocity, called terminal velocity.