The correct answer is A.
The equation relating the current and voltage across the primary and secondary coils of a transformer is
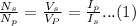 .
.
Equation (1) tells that the current is inversely proportional to the voltage and the number of turns. Equation (1) also tells us that voltage is directly proportional to the number of turns. In a transformer with more turns on the primary coil than on the secondary coil, the voltage decreases across the transformer, while the current increases.
In the case when the transformer has more turns in the secondary coil than in the primary coil, equation (1) tells us that the voltage will increase across the transformer while the current decreases.
This shows that in a transformer the output voltage and current are determined by the number of turns in the primary and secondary coil. The correct answer is A.