The rate constant from the Arrhenius equation is
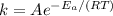
where
A = frequency factor
Ea = activation energy. It is assumed to be 50 kJ/mol, because it s not given.
R = gas constant = 8.31 J/(K-mol)
T = temperature, K
Evaluate Ea/R = 50000/8.31 = 6.0168 x 10³ K.
Therefore
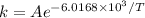
When T₁ = 600 K, k₁ = 6.1 x 10⁻⁸ s⁻¹
Therefore when T₂ = 800 K, the rate constant is
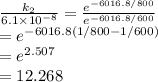
k₂ = 7.484 x 10⁻⁷ s⁻¹
The rate has increased by a factor of about 12.
Answer: The rate constant is approximately 7.5 x 10⁻⁷ s⁻¹