To solve an inequality, get the variable you're solving for on one side of the inequality and everything else on the opposite side.
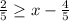
You get the x variable on it's own by undoing the operations done to it.
For example, if x is being multiplied by 5, you undo the multiplication operation by using the inverse of multiplication. Which is division.
We need to add
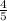
to both sides of the inequality to undo the subtraction operation done to x.
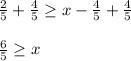
Convert the improper fraction into a mixed number.
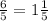
So, D 1 1/5 ≥ x is the answer.