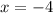Given the following equation:
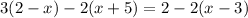
You can solve for the variable "x" and find its value as follows:
1. Apply the Distributive Property on both sides of the equation:
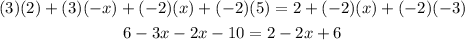
2. Add the like terms on both sides of the equation:
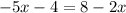
3. Apply the Addition Property of Equality by adding 4 to both sides of the equation:
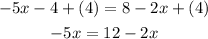
4. Now apply the Addition Property of Equality by adding this term to both sides of the equation:
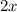
As follows:
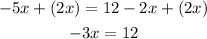
5. Finally, you can apply the Division Property of Equality by dividing both sides of the equation by -3:
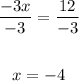
The answer is: