Answer: Option (C) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
An equation which relates the reduction potential of an electrochemical reaction with the standard electrode potential, temperature or concentration of chemical species undergoing the chemical reaction.
Mathematically,
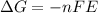
where
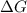 = Gibb's energy
= Gibb's energy
n = number of electrons transferred
F = Faraday's constant
E = electrochemical potential
Thus, we can conclude that in the equation E0 = -ΔG/nF, 'n' represents number of moles of electrons transferred.