Answer:
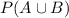 = 0.89
= 0.89
Explanation:
Using the formula:
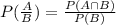 ....[1]
....[1]
where, A and B are events.
As per the statement:
Suppose A and B are dependent events.
If
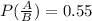 and P(B) = 0.2
and P(B) = 0.2
Substitute these in [1] we get;
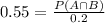
Multiply both sides by 0.2 we have;
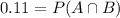
We know that:
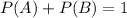
⇒
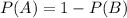
⇒

We have to find
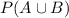
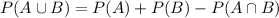
Substitute the given values we have;
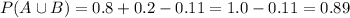
Therefore, the value of
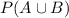 is, 0.89
is, 0.89