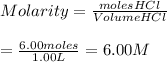Ans: D) 6.00 M
Given:
Volume of HCl, V(HCl) = 1.00 L
Volume of Ca(OH)2, V(Ca(OH)2) = 2.00 L
Molarity of Ca(OH)2, M(Ca(OH)2) = 1.50 M
To determine:
Molarity of HCl, M(HCl)
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction is:
2HCl + Ca(OH)2 → CaCl2 + 2H2O
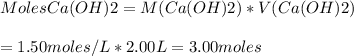
Based on the reaction stoichiometry:
2 moles of HCl reacts with 1 mole Ca(OH)2
Therefore, 3.00 moles of Ca(OH)2 would react with
=
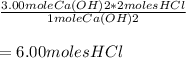
Given that V(HCl) = 1.00 L