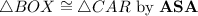Answer:
ASA/AAS
Skills needed: Triangle Geometry
Explanation:
1) When looking at Triangles, there are 5 ways to determine Congruence.
---> SSS - When all 3 sides of one triangle are congruent to the other. (The tick marks are used to signify the congruent sides - The sides with 1 tick are congruent to each other, the sides with 2 ticks are congruent to each other, and so on).
---> AAA - When all 3 angles of one triangle are congruent to the other. Again, tick marks are used to signify the congruent angles.
---> SAS - When 2 sides of a triangle are congruent, and the angle in between those two sides of the first triangle is congruent to the second triangle.
---> ASA - When two angles and the side in-between the two angles of one triangle are congruent to the other triangle.
---> AAS - When two angles and one of the two sides not in-between the two angles of the first triangle are congruent to the other triangle.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
As mentioned before, ticks are almost always used to display congruence of sides and angles.
The congruence sign is

----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2) In this problem,
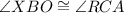 , meaning the angle denoted by XBO (B is the vertex, and X and O are the endpoints) is congruent to the angle denoted by RCA (C is the vertex, R and A are the endpoints)
, meaning the angle denoted by XBO (B is the vertex, and X and O are the endpoints) is congruent to the angle denoted by RCA (C is the vertex, R and A are the endpoints)
---> Also,
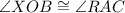 (Angle XOB is congruent to Angle RAC)
(Angle XOB is congruent to Angle RAC)
2 angles from the first triangle (
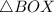 ) are found to be congruent in the 2nd triangle (
) are found to be congruent in the 2nd triangle (

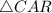 )
)
---------> ALSO:
-
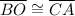 ---> One side from
---> One side from
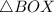 is congruent to
is congruent to
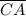 , which is from the other triangle.
, which is from the other triangle.
NOTE: This side is also in-between THE TWO ANGLES STATED BEFORE. This means that we have:
ASA ---> Since this has the side in-between the two angles.
ASA is the answer!