A. The square of the orbital period of a planet around the sun is proportional to the cube of the planet's orbital radius.
Step-by-step explanation:
Kepler's third law states that the square of the orbital period of a planet around the sun is proportional to the cube of the planet's orbital radius. This law can be expressed with the following equation:
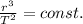
where
r is the orbital radius of the planet
T is the orbital period of the planet
This law tells that the ratio in the formula is constant for all the planets orbiting the same star, therefore if we know for example the orbital radius and period of one planet, and the radius of the orbit of a second planet, it is possible to calculate the orbital period of the second planet.