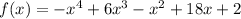Answer:
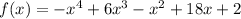
Explanation:
In order to find
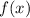 we need to integrate twice
we need to integrate twice
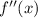 . So it's good to have in mind the next rules:
. So it's good to have in mind the next rules:
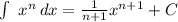
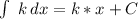
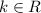
Where C, is an arbitrary constant.
The integral of the sum of two functions is equal to the sum of the integrals of these functions:
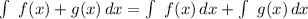
So, let's integrate
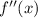 in order to obtain
in order to obtain
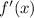 :
:
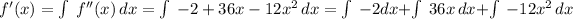
Integrating:
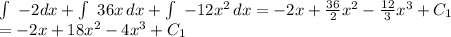
Evaluating the initial condition in order to find C1:
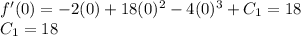
Now, let's integrate
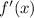 in order to obtain
in order to obtain
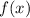 :
:
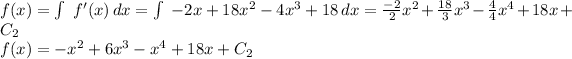
Evaluating the other initial condition in order to find C2:
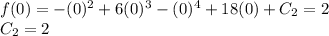
Knowing the value of C1 and C2, we can conclude that the function
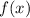 is given by:
is given by: