The astronaut’s mass does not change, while his weight decreases.
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass is an intrinsec property of an object that represents the amount of matter inside the object: so the mass of an object does not depend on the location, and this means that the mass of the astronaut is the same on Earth and on the Moon.
Instead, the weight of an object is given by:
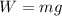
where
m is the mass of the object
g is the value of the gravitational acceleration
The value of g changes depending on the location: in fact, the value of g on the Moon is about 1/6 of the value of g on the Earth. By looking at the formula, we see that the weight W is directly proportional to g: therefore, since the moon's gravitational acceleration is less than Earth's, also the weight of the astronaut will be less on the moon, and more precisely it will be 1/6 of his weight on the Earth.