The Pythagorean states that when you take the two legs and square them and add them together, you get the same value as squaring the hypotenuse.
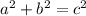
Where a and b are the legs and c is the hypotenuse.
The Pythagorean theorem is useful when finding a missing side of a right triangle.
For example, say we have a right triangle with the legs of 3 and 4.
But we do not the length of the hypotenuse.
Plugging in the values we do know, we can get the length of the hypotenuse.
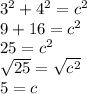
So, the length of the hypotenuse would be 5.