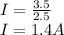Answer:
1.4A
Step-by-step explanation:
Ohm's law states the the current flowing through a metallic conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference applied across it provided that the temperature and other necessary physical conditions remain constant.
This law is mathematically rendered as follows;

where V is the potential difference, I is the current and R is the resistance of the conductor.
The current I could be determined by making it the subject of formula provided other parameters are known.

Given;
V = 3.5V
R = 3.5Ohms.
We then substitute these into equation(2) to obtain I.