Answer: The molarity of the NaOH solution is 0.5 M.
Step-by-step explanation:
Moles of
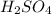 in 0.25 L of 2.00 M solution:
in 0.25 L of 2.00 M solution:
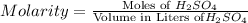
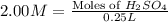
Moles of
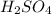 = 2.00 mol/L × 0.25 L = 0.5 moles
= 2.00 mol/L × 0.25 L = 0.5 moles
Moles of
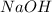 in 2.00 L of an unknown Molarity :
in 2.00 L of an unknown Molarity :
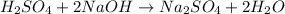
1 mole
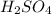 gives 2 moles of
gives 2 moles of
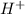 ions.
ions.
Then 0.5 mole
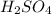 will give: 0.5 mol × 2 = 1.0 mol
will give: 0.5 mol × 2 = 1.0 mol
1.0 mol of
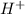 will neutralize the 1.0 mol of
will neutralize the 1.0 mol of
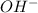 ions.
ions.
Moles of
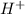 = Moles of
= Moles of
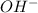 = 1.0 moles
= 1.0 moles
1 mol of
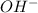 are produced by 1 mol of NaOH
are produced by 1 mol of NaOH
The 1 mole of
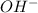 will be produced from = 1 mol of NaOH
will be produced from = 1 mol of NaOH
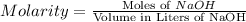
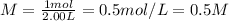
The molarity of the NaOH solution is 0.5 M.