Answer:
the distance of second ball will be 4 times more than the distance of first ball.
Step-by-step explanation:
Since both the balls are hit from ground level and reached again at ground then the horizontal distance covered by the ball must be equal to the range of projectile motion
As we know that range of projectile motion is given as
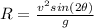
so here we can say that for the first ball is the speed is "v" then its distance on the ground will be
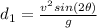
now for the other ball if the speed is double but the angle is same so we have
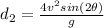
so the distance of second ball will be 4 times more than the distance of first ball.