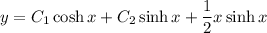For the nonhomogeneous ODE
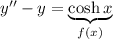
we're looking for a particular solution of the form
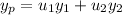
where
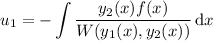
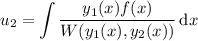
and
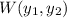
is the Wronskian of the two fundamental solutions.
We have
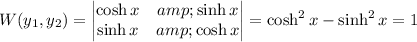
so we're left with
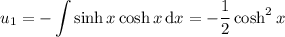
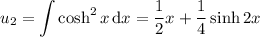
so that the particular solution is
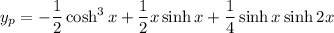
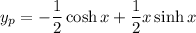
As
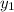
already accounts for the
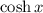
term in
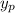
, we're left with the general solution