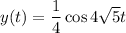Use Hooke's law to find the spring constant. If it takes 8N to stretch the spring by 0.1m, then
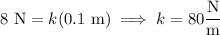
I'm going to assume the spring is fixed to a ceiling, and that any stretching in the downward direction counts as movement in the positive direction. The spring's motion is then modeled by
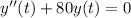
where
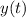
is the position of the spring's free end as it moves up and down. Solving this is easy enough: the characteristic solution will be
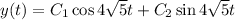
Given that the spring is stretched to a length of 1m (a difference of 0.25m from its natural length), and is released with no external pushing or pulling, we have the two initial conditions
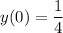
and
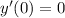
.
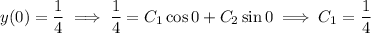
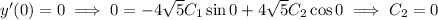
So the spring's motion is dictated by the function