Answer:
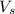 =0.0424m/s
=0.0424m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Using the law of the conservation of linear momentum P:

so:

where
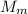 is the mass of the man,
is the mass of the man,
 is the initial velocity of the man,
is the initial velocity of the man,
 is the mass of the puck,
is the mass of the puck,
 is the initial velocity of the puck,
is the initial velocity of the puck,
 is the mass of the puck and the man and
is the mass of the puck and the man and
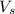 is the velocity of both after the collition.
is the velocity of both after the collition.
Replacing values, we get:

Finally, solving for
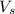 :
:
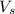 =0.0424m/s
=0.0424m/s