Step-by-step explanation:
(1). Given that,
Resistance
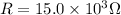
Voltage
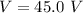
Using ohm's law
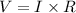
(a). Draw a circuit
(b).The current is defined as:
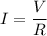 .....(I)
.....(I)
Here, V = voltage
R = resistance
I = current
Put the value of V and R in equation (I)
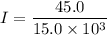
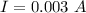
The current is 0.003 A.
(c). The power dissipated by the resistor will be
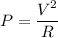
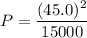
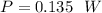
The power dissipated by the resistor will be 0.135 Watt.
(2). Given that,
Resistance
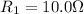
Resistance
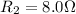
Resistance
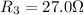
Voltage
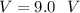
(a). Draw a circuit
(b). The equivalent circuit will be
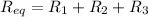
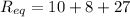
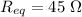
The current is defined as:
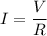 .....(I)
.....(I)
Here, V = voltage
R = resistance
I = current
Put the value of V and R in equation (I)
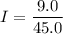
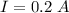
The current is 0.2 A.
(c). The voltage drop across each resistor in the circuit
The voltage drop across 10.0 ohm resistor,
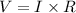
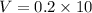
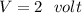
The voltage drop across 8.0 ohm resistor,
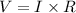
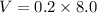
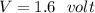
The voltage drop across 27.0 ohm resistor,
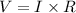
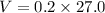
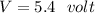
The voltage drop across each resistor in the circuit is 2 V, 1.6 V and 5.4 V.
(3). Given that,
Resistance
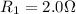
Resistance
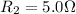
Resistance
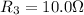
Voltage
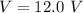
(a). Draw a circuit
(b). The equivalent resistance will be
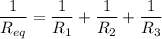
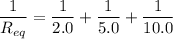
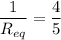
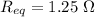
The equivalent resistance will be 1.25 ohm.
(c). The current passing through each resistor in the circuit.
The current passing through 2.0 ohm resistor
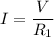
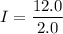
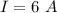
The current passing through 5.0 ohm resistor
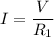
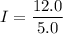
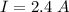
The current passing through 10.0 ohm resistor
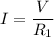
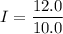
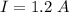
The current passing through each resistor in the circuit is 6 A, 2.4 A and 1.2 A.