Answer : The enthalpy change of the reaction is, -470.2 KJ/mole
Solution :
According to Hess’s law of constant heat summation, the heat absorbed or evolved in a given chemical equation is the same whether the process occurs in one step or several steps.
The balanced chemical reaction are,
(1)
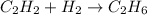

(2)
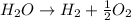
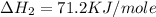
(3)
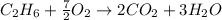
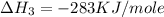
The balanced main chemical reaction will be,
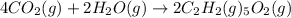
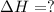
First reverse the reaction 3 then adding the twice of reaction 3, twice of reaction 1 and then subtracting four times of reaction 2 from the addition of two reaction 3 and 1, we get the enthalpy change of the reaction.
The expression for enthalpy change of the reaction is,
![\Delta H_(formation)=[2* \Delta H_3]+[2* \Delta H_1]-[4* \Delta H_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ggcvr7xn0tfik1lv0w49j16jty7si7ydwo.png)
where,
n = number of moles
![\Delta H_(formation)=[2* (283)]+[2* (94.5)]-[4* (71.2)]=470.2KJ/mole](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/vuz00nihl43sdru6ut56s0tv7s1if2dca0.png)
Therefore, the enthalpy change of the reaction is, -470.2 KJ/mole