Consider the differential equation
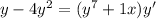
where y(0)=1 Solve this equation by the following method: First, find a suitable integrating factor to obtain an implicit solution F(x,y) = C. This implicit solution cannot be solved explicitly for y but it can be solved explicitly for x.