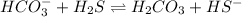Answer : The equilibrium system in which
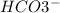 acting as a Brønsted-Lowry base is,
acting as a Brønsted-Lowry base is,
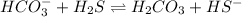
Explanation :
According to the Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base concept, an acid is a substance that donates protons and forming conjugate base and a base is a substance that accepts protons and forming conjugate acid.
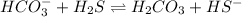
In this equilibrium system,
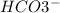 acting as a Brønsted-Lowry base which accepts protons and forming conjugate acid
acting as a Brønsted-Lowry base which accepts protons and forming conjugate acid
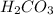 .
.
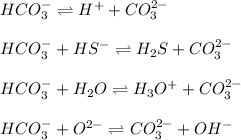
While in these equilibrium system,
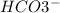 acting as a Brønsted-Lowry acid which donates protons and forming conjugate base
acting as a Brønsted-Lowry acid which donates protons and forming conjugate base
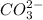 .
.
Hence, the equilibrium system in which
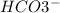 acting as a Brønsted-Lowry base is,
acting as a Brønsted-Lowry base is,