Answer:
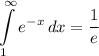
General Formulas and Concepts:
Calculus
Limits
Limit Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle \lim_(x \to c) [f(x) \pm g(x)] = \lim_(x \to c) f(x) \pm \lim_(x \to c) g(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/hcs1nne95gah4kjsf848sh4vnab8v42lwl.png)
Limit Property [Multiplied Constant]:
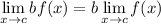
Differentiation
- Derivatives
- Derivative Notation
Derivative Property [Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [cf(x)] = c \cdot f'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/mathematics/high-school/s293bflxm18bvcg1l3en3cuunq0lisacx0.png)
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Integration
Integration Rule [Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 1]:
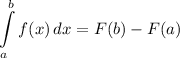
Integration Property [Multiplied Constant]:
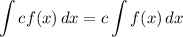
U-Substitution
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
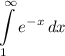
Step 2: Integrate Pt. 1
- [Integral] Rewrite [Improper Integral]:
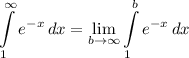
Step 3: Integrate Pt. 2
Identify variables for u-substitution.
- Set u:
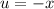
- [u] Differentiate [Basic Power Rule, Derivative Properties]:
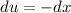
- [Bounds] Switch:
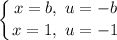
Step 4: Integrate Pt. 3
- [Integral] Rewrite [Integration Property - Multiplied Constant]:
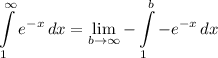
- [Integral] U-Substitution:
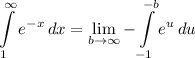
- [Integral] Rewrite [Limit Property - Multiplied Constant]:
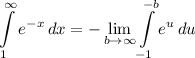
- [Integral] Exponential Integration:
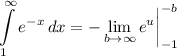
- Evaluate [Integration Rule - Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 1]:
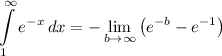
- Rewrite:
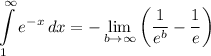
- Evaluate limit:
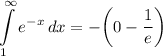
- Simplify:
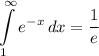
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Integration