Let x = negative real number ⇒x<0
from the statement above, we can generate an equation:
(x + 5)² = 48
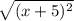
=
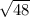
⇒ eliminate the square by getting the square root on both sides
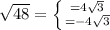
⇒ the perfect square of a real number has one positive real number and a negative real number
transposing 5 to other side, we will arrive at two (2) values for x:
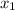
= -5 - 4√3 =
-11.928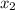
= -5 + 4√3 = 1.928
Since we are only looking at the negative real number, our answer will be -11.928, also equal to -5 - 4√3.