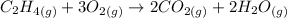
We will use the standard-state energy of formation to calculate the reaction Gibbs free energy. We first have to calculate the entropy and the enthalppy of the reaction using the standard state conditions.
![\begin{gathered} \Delta H\degree=\Sigma\Delta H\degree_{f\text{ }products}-\Sigma\Delta H\degree_{f\text{ }reactants} \\ \Delta H\degree=(2*-393.5kJmol^(-1))+(2*-241.8kJmol^(-1))-(3*0)+(52.3kJmol^(-1)) \\ \Delta H\degree=-1,218.3\text{ }kJmol^(-1) \\ \\ \Delta S\operatorname{\degree}=\Sigma\Delta S\operatorname{\degree}_{f\text{p}roducts}-\Sigma\Delta S\operatorname{\degree}_{f\text{r}eactants} \\ \Delta S\operatorname{\degree}=(2*213.6Jmol^(-1)K^(-1))+(2*188.7Jmol^(-1)K^(-1))-(3*205.0Jmol^(-1)K^(-1)) \\ +(219.5Jmol^(-1)K^(-1)) \\ \Delta S\operatorname{\degree}=-29.9Jmol^(-1)K^(-1) \end{gathered}]()
We will now substitute the values into the free energy equation to determine Gibbs energy for the reaction:
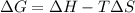
But first we need to convert the units for entropy S and the temeprature to Kelvin:
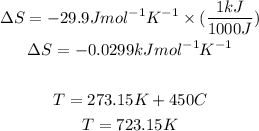
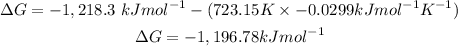
Answer: The free-energy is -1,196kJmol^-1.