Answer : The amount of heat produced during the combustion of hexane per mole is 4109.79 kJ/mole.
Explanation :
In this problem we assumed that heat given by the hot body is equal to the heat taken by the cold body.
Formula used :
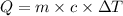
where,
Q = heat absorb = ?
m = mass of calorimeter = 1.900 kg = 1900 g
c = specific heat of calorimeter =
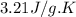
 = change in temperature = 4.542 K
= change in temperature = 4.542 K
Now put all the given value in the above formula, we get:
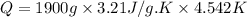
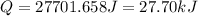
Now we have to calculate the moles of hexane.
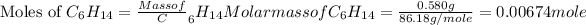
Now we have to calculate the heat produced during the combustion of hexane per mole.
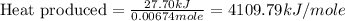
Therefore, the amount of heat produced during the combustion of hexane per mole is 4109.79 kJ/mole.