Through de Broglie's hypothesis, we can express the relationship between a particle's wavelength and momentum through the equation below.
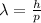
where h is the Plank's constant equivalent to 6.626 x 10⁻³⁴ J.s. Recall that momentum, p, can be computed as
p = mv
where m is the mass and v is the velocity of the particle. Now, we have a rock with a mass of 60.0 g or 0.06 kg and a velocity of 40.0 m/s. Now, its de Broglie wavelength is
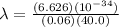
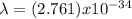
Therefore, the rock's de Broglie's wavelength is 2.761 x 10⁻³⁴ m.
Answer: 2.761 x 10⁻³⁴ m