Naturally, any integer
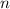
larger than 127 will return
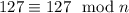
, and of course
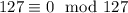
, so we restrict the possible solutions to
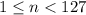
.
Now,

is the same as saying there exists some integer
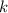
such that
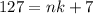
We have
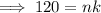
which means that any
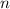
that satisfies the modular equivalence must be a divisor of 120, of which there are 16:
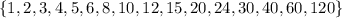
.
In the cases where the modulus is smaller than the remainder 7, we can see that the equivalence still holds. For instance,
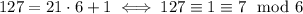
(If we're allowing
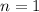
, then I see no reason we shouldn't also allow 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.)