First, find the molality of the solution.
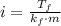
Where k is the molal freezing point, which is 1.86 C/m for water.
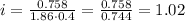
The equilibrium constant Ka would be
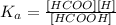
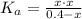
Then, to find x.
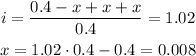
Once we have x, we can obtain the constant Ka
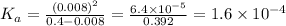
Therefore, the constant Ka of the reaction is 1.6x10^-4.