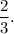Answer: The answers are:
(a) The dilation is a reduction of the original figure.
(b) The scale factor of dilation is
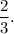
Step-by-step explanation: We are given a dilation from ΔMSV to ΔM'S'V'.
We are to check whether the dilation is a reduction or an enlargement of the original figure. Also, to find the scale factor of dilation.
We know that if a figure is dilated to form the image figure, then the scale factor of dilation is given by
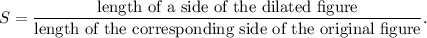
If S < 1, then the dilation will be a reduction and if S > 1, then the dilation will be an enlargement.
We can note from the figure that
the co-ordinates of the vertices of the original triangle MSV are M(-3, 3), S(6, 3) and V(3, -3),
and the co-ordinates of the dilated triangle M'S'V' are M'(-2, 2), S'(4, 2) and V'(2, -2).
So, the lengths of the corresponding sides MS and M'S' of both the original and dilated figures are calculated using distance formula as follows:
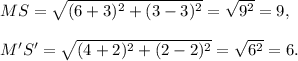
Therefore, the scale factor of dilation is given by
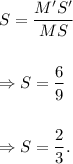
Since S < 1, so the dilation is a reduction.
Thus, the required results are
(a) The dilation is a reduction of the original figure.
(b) The scale factor of dilation is