Given the equation:
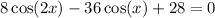
Let's solve the equation over the interval [0, 2π).
Let's simplify the equation:
Apply the double angle identity
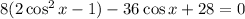
Apply distributive property:
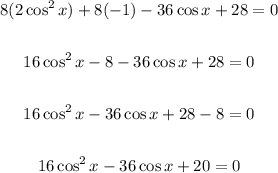
Factorize:
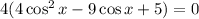
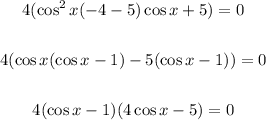
Take the individual factors and equate to zero:
• cos x-1 = 0
,
• 4cosx- - 5 = 0
Solve each factor for x:
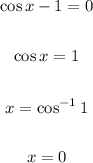
Subtract the reference angle from 2π
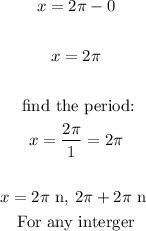
Second factor:
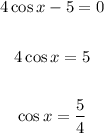
• The range for cosine is -1 ≤x ≤ 1.
Since cos x is not in the range, there is no solution,.
Input 0 for n in 2πn and solve:
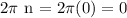
Therefore, the interval contains:
x = 0
ANSWER:
x = 0