What we're looking for here is the gas sample's molar mass given its mass, pressure, volume, and temperature. Recalling the gas law, we have
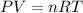
or
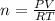
where R is
0.08206 L atm / mol K, P is the given pressure, T is the temperature, and V is the volume.
Before applying the values given, it is important to make sure that they are to be converted to have consistent units with that of R.
Thus, we have
P = 736/ 729 = 0.968 atm
T = 28 + 273.15 = 301.15 K
V = 250/1000 = 0.250 L
Now, applying these converted values into the gas law, we have
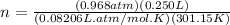
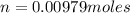
Given that the mass of the sample is 0.430 g, we have
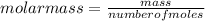
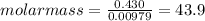
Thus, the gas sample has a molar mass of 43.9 g/mol.