The frequency distribution tell us how often something happened. In our case, we have some fruits which appear in our list
Lets count them:
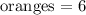
and
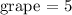
and
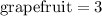
and finally
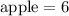
As we can corroborate in the picture:
Now, with this numbers, we can construct our frequency distribution table:
The frequency of a particular data value is the number of times the data value occurs and the relative frequency is the ratio between each number to the total. In our case, we must multiple by 100% because we need the answer as percent.
Now, lets draw a Pareto chart. A Pareto chart is a bar graph. The lenghts of the bars represent frequency and are arranged with the longest bars on the left and the shortest to the right in order to visually depicts which situacions are more significant.
Pareto chart: