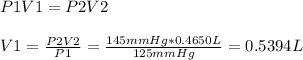Answer:
Initial volume of container = 0.5394 L (≅0.539 L)
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Initial pressure of gas, P1 = 125.0 mmHg
Final pressure of gas, P2 = 145 mmHg
Final volume, V2 = 0.4650 L
To determine:
The initial volume V1 occupied by the gas
Step-by-step explanation:
Based on the ideal gas equation
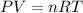
where P = pressure, V = volume ; n = moles of gas
R = gas constant, T = temperature
At constant n and T, the above equation becomes:
PV = constant
This is the Boyle's law
Therefore: