Answer:
The equation that describes the motion of the object is
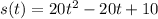
Explanation:
It is given that,
Acceleration of the object at time t is:
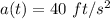
Initial velocity or velocity at t = 0,
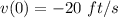
Initial position or position at t = 0,
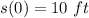
Since,
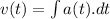
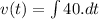
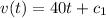 ............(1)
............(1)
At t = 0,
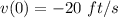
→
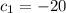
Equation (1) becomes :
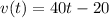
Since,
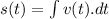
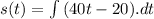
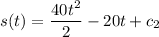 ............(2)
............(2)
At t = 0,
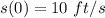
→
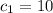
Equation (2) becomes:
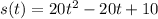
Hence, this is the required solution.