Answer: The base dissociation constant for the equation is
![K_b=([BH^=][OH^-])/([B])](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/obif99q0z58ivatgzqbr65xyux9esedj5y.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
Base dissociation constant,
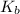 exists when a weak base is dissolved in water. It is expressed as the ratio of molar concentration of the products and the molar concentration of the reactants raised to power their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
exists when a weak base is dissolved in water. It is expressed as the ratio of molar concentration of the products and the molar concentration of the reactants raised to power their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
For the dissociation of a weak base, the equation follows:

The equilibrium constant for the above equation:
![K_(eq)=([BH^=][OH^-])/([B][H_2O])](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/z3xbiowxzw7d9nabvczddkwv0n238b75x5.png)
Concentration of water is very large and is taken as constant.
![K_(eq)* [H_2O]=([BH^=][OH^-])/([B])](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/y8avtvym0abl90t7ipn0yeq1w35481lv9y.png)
Hence, the equation becomes:
![K_b=([BH^=][OH^-])/([B])](https://img.qammunity.org/2018/formulas/chemistry/high-school/obif99q0z58ivatgzqbr65xyux9esedj5y.png)