Answer:
The value of
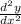 at (2,2) is
at (2,2) is
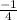 .
.
Explanation:
The given equation is
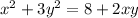
Differentiate with respect to x.
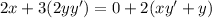
Here,
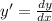
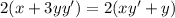
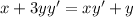
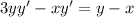
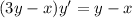
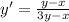
The value of first derivative at (2,2) is
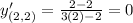
Differentiate with respect to x. Using quotient rule we get,
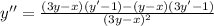
The value of second derivative at (0,0) is
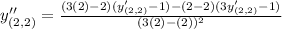
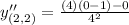
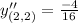
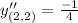
Therefore the value of
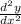 at (2,2) is
at (2,2) is
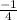 .
.